If your website were a building, technical SEO would be the blueprint and infrastructure, quietly doing the heavy lifting behind the scenes. No matter how beautiful the design or persuasive the content, if the foundation is weak or the wiring is faulty, things start to crumble. Search engines won’t find you, users won’t stay, and your efforts go unnoticed.
Technical SEO ensures your site is fast, crawlable, indexable, and secure. It’s what ensures your content is seen and ranked in the first place. On-page SEO tells search engines what you’re about. Off-page SEO tells them why you’re trustworthy. But technical SEO makes sure they can actually get there.
And in 2025, it matters more than ever. With Google’s Core Web Vitals, mobile-first indexing, and AI-powered search reshaping visibility rules, relying on the basics just won’t cut it. You need a well-structured, performance-optimized site that clears all the technical hurdles before your content even has a chance to compete. Here’s how to build a future-proof site that search engines (and users) love.
Website Architecture and Crawlability
Imagine your website as a city, and search engine spiders as tourists attempting to get around it. If your streets are disorienting and maps are absent, they’ll become lost, or worse, straight-up leave. That’s why website architecture and crawlability are at the core of successful technical SEO.
Search engines use crawlers to find and index material. A logical site structure, such as Home > Category > Subcategory > Page, increases user satisfaction and makes it easier for crawlers to locate and rank your pages.
- The flatter your site architecture, the quicker search engines can burrow through your website without encountering a dead end.
With URLs, simplicity is the key. Simple, keyword-based URLs such as “/blog/technical-seo-guid” are much better than cluttered strings such as “/index.php?id=12345.”
- Organized URLs assist both bots and humans in knowing where they are and what to anticipate.
XML sitemaps are blueprints for search engines. They inform Google where your most critical pages are and when they were last updated.
- Updating your sitemap and submitting it through Google Search Console (GSC) is one of the simplest technical SEO actions to take for maximum impact.
Robots.txt is your site’s bouncer. It instructs crawlers where they can come in and where they can’t. Just don’t end up blocking your whole site by accident (yes, it happens more than you’d imagine).
Lastly, canonical tags prevent duplicate content horrors. If you have the same content on more than one URL, canonical tags inform Google which one is the “official” version, so the other versions don’t eat into your rankings.
Core Web Vitals and Site Performance
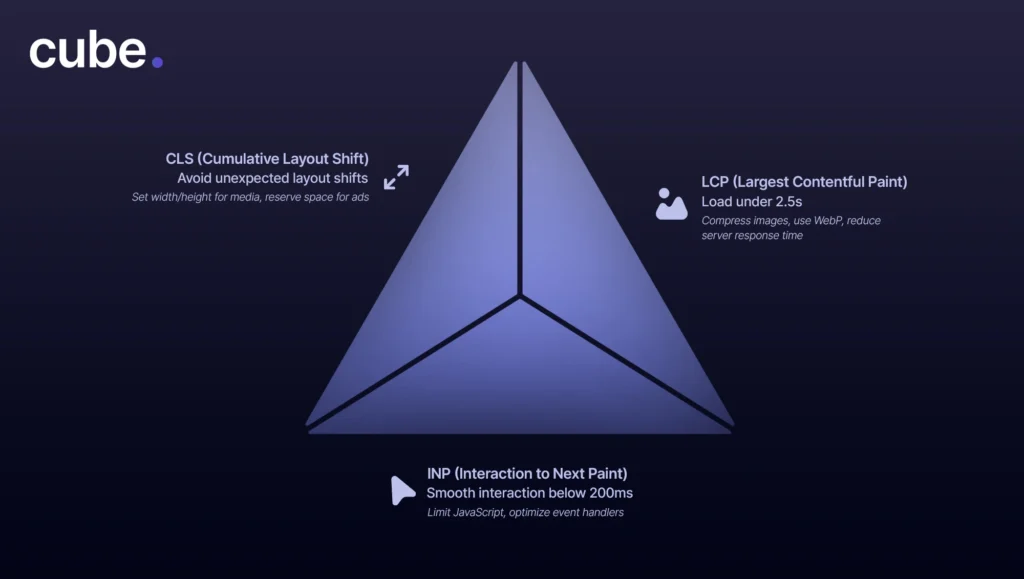
Site performance has officially graduated from a metric that was “nice to have” to a “critical SEO ranking factor.” Google’s Core Web Vitals are now the measuring stick for user experience, focusing on speed, interactivity, and visual stability. If your site isn’t keeping up, you’re not just losing ranking, you’re losing visitors. Let’s break down why site performance can make or break your online presence.
What Are Core Web Vitals, and Why Are They Important?
Core Web Vitals are Google’s method for assessing real-world user experience. They assess how fast your site loads, reacts, and remains visually stable when in use. Consider them the website performance checkup and a critical aspect of technical SEO optimization.
Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) Optimization
LCP measures the speed at which the largest item visible on the page, most commonly an image or a header, is loaded. Well below 2.5 seconds is good. Opt for compressed images, serve modern file formats (e.g., WebP), and minimize server responses. Each millisecond counts.
First Input Delay (FID) and Interaction to Next Paint (INP) Performance Improvements
FID gauges responsiveness to the initial user interaction, but it’s being replaced by INP, which has a more comprehensive view of input responsiveness. Minimize input delays by limiting JavaScript execution time, delaying unused scripts, and optimizing code efficiency.
Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) and How to Minimize It
CLS quantifies how far your content moves during loading. Unstable layouts are annoying and damage user trust. Hold space for images and ads, don’t inject content dynamically, and apply explicit height and width attributes to visual elements.
Optimizing Time to First Byte (TTFB)
TTFB refers to the amount of time taken by your server to respond to a request. A slow TTFB slows down your LCP and, consequently, your entire website. Leverage a trustworthy content delivery network, optimize your backend code, and limit heavy plugins or third-party scripts.
Lazy Loading Images and Videos for Better Performance
Lazy loading postpones the loading of media until it’s actually required, cutting down on the time of initial load and saving bandwidth. This makes your site responsive and agile, particularly on mobile. It’s a requirement for media-rich pages.
Mobile SEO and Responsive Design
If your website isn’t mobile-friendly, it’s essentially invisible in search. With Google’s mobile-first indexing now the norm, technical SEO optimization needs to begin with small screens in mind. It’s not merely about fitting your content onto a phone screen; it’s about building seamless, lightning-fast experiences that actually convert.
Mobile-First Indexing: What It Means and How to Optimize for It
Google now predominantly uses the mobile version of your site for indexing and ranking. Ensure content, metadata, and structured data on mobile matches the data on desktop. Avoid hiding crucial elements on smaller screens.
Best Practices for Responsive Web Design
Responsive design makes your site smoothly fit any screen size. Employ flexible grids, scalable graphics, and CSS media queries to provide an optimal user experience for every device. Say “Goodbye” to pinching and zooming and “Hello” to tidy, readable content that works.
Accelerated Mobile Pages (AMP): Are They Still Relevant?
AMP was once the darling of mobile SEO, but now its use is situational and optional. Although it can increase speed, it compromises design freedom and increases dependence on Google’s structure. Instead, most are opting for high-performance responsive sites without AMP. It’s less about structure and more about speed and usability.
Optimizing Navigation and UX for Mobile Users
Thumbs govern the mobile universe. Put simple tap targets, sticky navs, and reduced navigation at the top. Don’t show endless dropdowns or minuscule buttons. Your mobile UX must predict frustration and cut it off before it begins.
Mobile Page Speed and Performance Improvements
Mobile users are usually impatient. Optimize images, utilize browser caching, reduce redirects, and deliver content over a CDN to enhance performance. Utilize tools such as Google’s PageSpeed Insights to recognize and optimize slow-loading pieces of content responsible for driving bounce rates sky-high.
Secure and Accessible Sites
In 2025, search engines are more focused than ever on user safety and accessibility. That means that technical SEO now has two more pillars: security and accessibility.
The Role of HTTPS in SEO and Website Security
Google has made it as clear as day: safe websites rank higher in search results. HTTPS does more than display a green padlock; it encrypts information and protects visitors from worrying about interception. A website operating over HTTP is viewed as outmoded and possibly dangerous, which can damage rankings and users’ trust directly.
SSL Certificates: Why They’re Vital for Ranking
An SSL certificate is the engine behind HTTPS. Without it, search engines will mark your site as “Not Secure,” potentially scaring off users and damaging your credibility. It’s also a confirmed ranking signal. Whether you’re running a blog or an e-commerce empire, SSL is a non-negotiable piece of technical SEO optimization.
How to Make Your Website Accessible (ADA & WCAG Compliance)
Accessibility is not only the right thing to do, it’s a good strategy. By adhering to ADA and WCAG standards (such as good contrast levels, alt attributes, and keyboard accessibility), your content is accessible to everyone, including people with disabilities. Search engines reward accessibility. They are crawling accessible items more easily and treat them as quality signals.
The Impact of Accessibility on Search Rankings
Although accessibility isn’t a direct ranking signal (yet), it feeds into important metrics such as time on site, bounce rate, and user engagement — all of which impact how well your site ranks in search. More accessible = more usable = better SEO.
Indexing and JavaScript SEO
Modern websites increasingly rely on JavaScript to deliver rich, interactive user experiences. But what works well for users doesn’t always work well for search engines. Unlike static HTML, JavaScript-driven content can create challenges for search engine bots, which may struggle to render or index certain elements correctly if not implemented properly.
That’s why technical SEO today demands more than just traditional best practices; it requires a solid understanding of how search engines process JavaScript. From rendering delays to dynamic content loading, even small missteps can result in critical content being missed or misinterpreted by crawlers.
If you’re using frameworks like React, Angular, or Vue, ensuring proper server-side rendering, hydration, or pre-rendering becomes essential. Without that, your most important pages might never appear in search results, no matter how well they’re written or designed.
In short, mastering JavaScript SEO is no longer optional. It’s a key part of making sure your website is truly discoverable.
How Google Processes JavaScript-Based Websites
Googlebot is better at rendering JavaScript now, yet it still lags in processing plain HTML. This slowdown can lead to content being lost or crawled incorrectly if your scripts aren’t crawl-friendly.
The Difference Between Client-Side and Server-Side Rendering
Client-side rendering (CSR) is JavaScript in the browser. It is good for users, not so much for bots. Server-side rendering (SSR) does most of the work before your content hits the browser, which is more convenient for Google to crawl and index at high speed and in its entirety.
Best Practices for JavaScript-Heavy Websites
Use SSR or hybrid rendering techniques where feasible, preload important resources, and do not depend solely on JavaScript to render important content. Lazy loading is awesome, but not if it conceals what Googlebot should see.
Troubleshooting Common JavaScript SEO Issues
Use the “URL Inspection” feature in GSC to see what Google sees. If it can’t be rendered by Google, your users most likely can’t either.
Structured Data and Schema Markup
Structured data is similar to providing search engines with a cheat sheet. It makes it easier for them to comprehend your content and present it better. It’s not a ranking factor, per se, but rich results? Those improve CTRs. And that’s what technical SEO optimization is all about.
What Is Structured Data, and Why Does It Matter?
Structured data organizes information in a search engine’s favorite way. It’s like providing them with a map of your content, instead of leaving them to guess. The outcome? Rich results such as stars, prices, FAQs, and event listings in search.
Types of Schema Markup (LocalBusiness, FAQ, Product, etc.)
Various schema are used for different purposes. LocalBusiness schema increases local visibility, FAQ schema gains collapsible answers in search, and Product schema highlights availability, price, and reviews. Pick according to your business objectives.
How Structured Data Affects Rich Results in SERPs
Rich results dominate. Whether a recipe with star ratings or a product with inventory information, schema makes your listings more clickable. And although it doesn’t rank higher directly, improved engagement signals do fuel the ranking machine.
Implementing Schema Using JSON-LD
JSON-LD is Google’s favorite. It’s tidy, apart from HTML, and simple to maintain. You can implement it by hand or via CMS plug-ins, just ensure your structured data remains current and on point.
Testing and Validating Structured Data with Google’s Tools
Utilize Google’s Rich Results Test and the Schema Markup Validator to check. Errors or warnings? Correct them before the bots come knocking.
Site Speed and Performance Optimization
Let’s face it—nobody enjoys waiting. For the world of SEO, speed isn’t an added benefit, it’s a ranking factor. Slow sites anger users, raise bounce rates, and can ruin the best of content planning. Technical SEO optimization and speed are therefore two peas in a pod.
Why Speed Matters for SEO and Conversions
Google has made it clear: speed affects rankings. But beyond the bots, it’s about humans as well. A one-second page load time delay can decrease conversions by 7%-ouch. Sites that load quickly make for smoother experiences and more engagement, which Google adores.
Tools for Measuring and Improving Site Speed
We’re in a golden era of performance tooling. Google PageSpeed Insights, Lighthouse, and GTmetrix give you rich analysis of what’s holding you back-and how to make it better. Spoiler: it’s most likely JavaScript or uncompressed images.
Image Compression and Next-Gen Formats (WebP, AVIF)
Pictures tend to be the largest contributors to bloat. Compress them without sacrificing quality, and store them in up-to-date formats such as WebP or AVIF. They’re lean and mean, load quickly, and are supported by most browsers. Bonus: Google favors them.
Caching Strategies for Load Times
Browser caching instructs a visitor’s browser to retain parts of your site, so subsequent visits are quicker. Server-side caching cuts down on having to regenerate pages each time. It’s similar to boosting your site’s memory.
Slowing Down Server Response Times and Improving Database Queries
Your TTFB (Time to First Byte) says a lot about your backend health. If it’s sluggish, it’s time to review your hosting, reduce bloated code, and optimize those database queries. Query bloat and slow servers = slow SEO gains.
Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) and Their SEO Benefits
CDNs spread your site out across several servers globally, so users have quicker load times regardless of where they are. Bonus: CDNs also enhance uptime, security, and scalability-all positives for both SEO and user trust.
URL Optimization and Redirect Management

URLs are not simply online addresses. They’re small signposts for humans and search engines alike. With proper execution, they can increase your visibility; with improper execution, they can sink your crawlability. Let’s get that digital roadmap cleaned up.
The Importance of Clean and SEO-Friendly URLs
We all love clean and well-organized addresses. Search engines do too. Brief, descriptive URLs that contain pertinent keywords (not stuffed) are simpler to read, recall, and rank. Steer clear of random strings such as “site.com/p=12345” and opt for “site.com/technical-seo-tips.”
Properly Handling 301 vs. 302 Redirects
Not all redirects are the same. A 301 redirect tells Google, “Hey, this move is permanent,” while a 302 says, “Temporary redirect.” Using the wrong one can confuse crawlers and lead to ranking drops. Always use 301s when retiring or consolidating content, and 302s when you are temporarily redirecting users to another page but plan to bring the original page back.
Identifying and Fixing Redirect Chains and Loops
A redirect chain is similar to sending a person through three airports to cross the town. It is inefficient and frustrating. Redirect loops? Worse yet, both users and bots get stuck in an infinite loop. Audit regularly and ensure redirects point straight to the ultimate destination.
Avoiding and Resolving Soft 404 Errors
A soft 404 is a page that appears normal to users but sends a message to Google that nothing is here. This is wasting crawl budget and damaging your SEO. Always return an actual 404 status for deceased pages, or preferably, redirect to a relevant resource if possible.
Handling Orphaned Pages and Crawl Budget Optimization
Orphaned pages (pages that have no internal links) are similar to having a secret room in your home. Without Google being able to see them, they won’t get indexed. Link every page to your internal linking plan and optimize crawl paths to get the maximum out of your website.
Duplicate Content and Canonicalization
Duplicate content may not land you an outright penalty from Google, but it will make search engines confused. And that equates to watered-down rankings, irregular indexing, and lost traffic opportunities. Let’s sort that mess out.
Common Causes of Duplicate Content
Sometimes, your own site architecture can work against you. Duplicate content often creeps in through things like printer-friendly pages, session IDs in URLs, HTTP vs. HTTPS inconsistencies, or www vs. non-www versions of the same page. Even eCommerce filters and faceted navigation can unintentionally create dozens of near-identical URLs, diluting SEO value and confusing search engines.
How to Use Canonical Tags Effectively
Canonical tags are your method of saying to search engines, “This is the original, stay with it.” Add a canonical tag (rel=\”canonical\”) to the preferred version of a page to merge link equity and prevent competing with yourself in the SERPs. It’s SEO housekeeping, and it’s not optional.
Best Practices for Handling Paginated Content
Pagination is UX wonderful, but terrible pagination configurations are SEO hell. Use rel=”next” and rel=”prev” (though Google has abandoned support, they’re still good for organization), or canonicalize a view-all page if it’s appropriate. Ensure that every paginated URL has different content or at least good signals.
Handling URL Parameters and Dynamic Content
Tracking codes, filters, sort orders; they all generate ugly URLs that appear different but deliver the same content. Utilize Google Search Console’s URL Parameters tool or set up your CMS to minimize parameter chaos. Always utilize canonical tags or meta directives to direct bots to the primary version of your content.
International and Multilingual SEO
Going global is exciting, but it also means your SEO game needs to speak more than one language (literally). Whether you’re targeting Tokyo, Toronto, or Tulum, international SEO ensures your content reaches the right audience, in the right language, and in the right domain.
Optimizing for Global Search Engines
Google might dominate the majority of the internet, but in nations such as China and Russia, Baidu and Yandex are the MVPs. Each search engine has its own unique features. Baidu prefers simplified Chinese and quickly loading pages hosted in China, while Yandex prioritizes user behavior. Know your audience and cater your strategy to it accordingly.
Hreflang Tags: What They Are and How to Use Them
Hreflang tags inform search engines, “Hey, this content is also in Spanish!” Adding hreflang annotations within your HTML or sitemap helps Google return the correct language version to users depending on their location and browser settings. No more confusing your French users with your English homepage.
Typical Multilingual SEO Blunders (And How to Steer Clear Of Them)
Mistake #1? Using Google Translate to translate content and close up shop. Bad translations kill UX and rankings. Other blunders include omitted hreflang tags, failing to localize metadata, and serving the incorrect language version through automatic redirects. The solution? Employ native speakers, properly set hreflangs, and always test the user experience in every market.
Organizing International Sites: ccTLDs, Subdirectories, or Subdomains
When expanding internationally, the organization counts.
- ccTLDs (such as .fr or .de) have strong local trust signals but are expensive and more difficult to maintain.
- Subdirectories (/fr/, /es/) are friendly to SEO and simple to maintain under a single domain.
- Subdomains (fr.example.com) provide flexibility, although they can divide SEO equity.
Choose the structure that best meets your team’s resources and long-term objectives, and adhere to it regularly.
Log File Analysis for SEO
Log files may not be the best to look at, but they’re SEO gold. Imagine them as your site’s black box, chronicling every step search engine bots take. Need to know how Googlebot views your site? This is where you look.
What Is Log File Analysis, and Why Is It Important?
Log file analysis is the act of checking server logs to observe how search engines (and users) behave on your site. It provides answers such as: Which pages are crawled? How frequently? Are crawlers wasting time on non-essential URLs? It’s like virtual surveillance, but SEO it.
How to Access and Analyze Server Logs
You’ll typically access logs via your hosting provider or server admin panel. Once in, use tools like Screaming Frog Log File Analyzer, Logz.io, or even plain old Excel to parse through entries. You’ll be looking at user agents, timestamps, URLs requested, and status codes. Nerdy? Yes. Invaluable? Also yes.
Identifying Crawl Frequency and Search Engine Behavior
Log files enable you to view how frequently various bots are visiting, what they’re prioritizing, and if they’re targeting the correct URLs. If Googlebot is spending excessive time on trash pages or bypassing your moneymakers, it’s time for a crawl budget intervention.
Detecting and Fixing Crawl Errors and Bottlenecks
You can capture trends such as continuous 404s, 500 errors, or rogue redirects. These errors consume the crawl budget and hinder indexing. Catching them early means you enhance crawl efficiency and get your best content the visibility it needs.
Advanced Technical SEO Strategies
Now that you’ve mastered the basics, it’s time to lift the hood on the next-gen techniques shaping the future of AI-assisted search. From AI wizardry to decentralized search engines, advanced technical SEO is where geek meets genius.
AI-Driven SEO Tools and Automation
The era of keyword spreadsheets and manual audits is being replaced by more intelligent solutions. Software such as Cube AI is leveraging artificial intelligence to scan SERPs, audit websites, and even create optimization recommendations quicker than you can say “ranking drop.” Technical SEO tasks are automated, saving time and gray hairs.
The Role of Machine Learning in Search Ranking
Google’s algorithms have evolved far beyond static rules. Powered by machine learning, search engines now adapt rankings in real time, based on user behavior, content relevance, and contextual signals. In today’s landscape, it’s not just about optimizing for keywords, but for intent. That means your content and technical foundation must evolve accordingly. SEO is no longer just a checklist; it’s behavioral science.
How Web3 and Decentralized Search Might Affect SEO
Although still nascent, Web3 brings decentralized platforms and blockchain search engines that may revolutionize content indexing and discovery. It’s speculative, sure, but innovative SEOs already are eyeing how protocols such as Presearch and the idea of digital identity may alter the SEO world.
The Importance of Entity-Based Search and Knowledge Graphs
Search engines now care less about keywords and are more fixated on entities—people, locations, brands, and concepts – linked in an organized web. Organizing your content to emphasize entities (and links between them) through schema, internal linking, and concise context can get your site listed in Google’s Knowledge Graph and semantic search results. It’s all about being recognized as the expert.
Monitoring and Maintaining Technical SEO

Technical SEO is not a one-time fix. Regular monitoring and maintenance are absolute necessities for a high-performing website.
Google Search Console for Monitoring Technical SEO Issues
If you’re not regularly using Google Search Console (GSC), you’re flying blind. GSC provides information on crawl errors, indexing status, Core Web Vitals, mobile usability, and more. It’s the direct line between you and Google. At Cube, both AI and human experts are monitoring your GSC data to continuously update your SEO strategy and implement fixes.
Setting Up Automated SEO Monitoring Alerts
Don’t wait until traffic tanks before you act. Utilize tools like Google Alerts to track abrupt changes, broken pages, or surprise dips in visibility. Automation prevents issues from snowballing into ranking nightmares.
Regular Maintenance Checklist for a Technically Solid Website
Let’s discuss the routine checkup. Your checklist must include:
- Monthly site speed audits
- Repairing crawl errors from GSC
- XML sitemap updates
- Checking structured data and schema
- Canonical validation and redirects
- Double-checking mobile accessibility and usability
Stay ahead, and your site remains sharp.
Let Cube AI Take Care of Your Site’s Tech SEO
Technical SEO is the backbone of your website’s search engine visibility. From crawlability and Core Web Vitals to structured data and log file analysis, these are ranking factors dressed in code.
If you wish to remain competitive in 2025, here’s your game plan: audit frequently, automate smartly, and optimize regularly. Begin with a clean site architecture, accelerate the pace, and get Google’s bots to feel at home.
And if it’s still too much for you? Don’t panic-that’s where Cube enters the picture. Whether you’re struggling to interpret GSC signals or execute high-level technical SEO actions, we’ve got you covered with continuous monitoring and practical, data-based solutions that deliver results.
Do you want to know more about how Cube AI can improve your site health? Book a demo call today.


